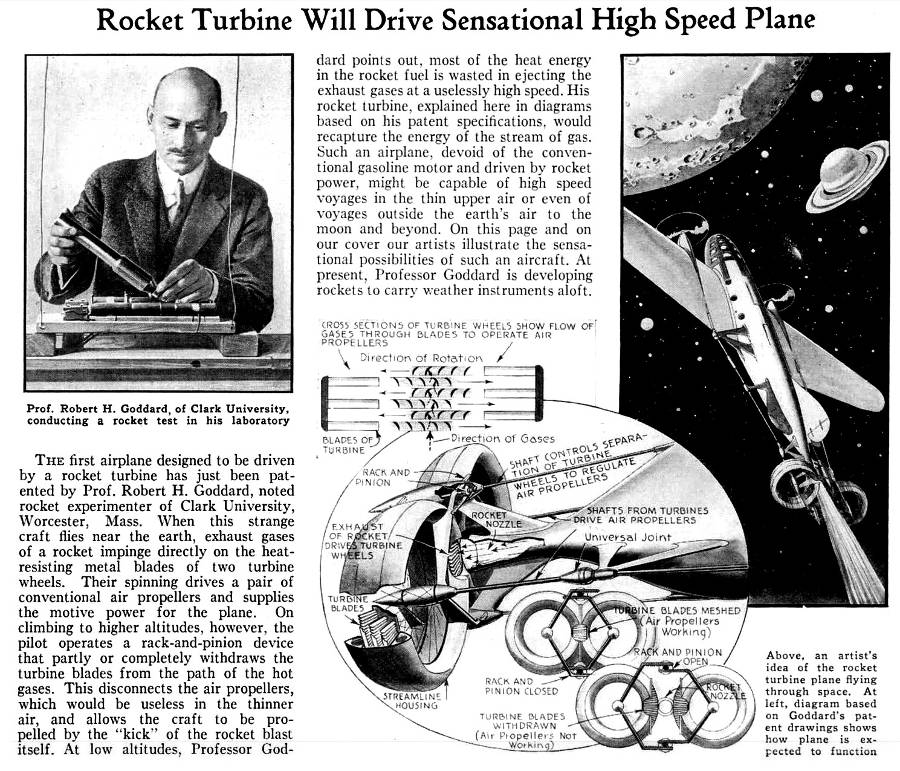
Prof. Goddard’s Turbine Rocket Ship For Flight To Moon, from Popular Science, December 1931
Tag: Moon
Popular Science, Dec, 1931
Shoot the Moon, 1920
The Washington Times, January 25, 1920
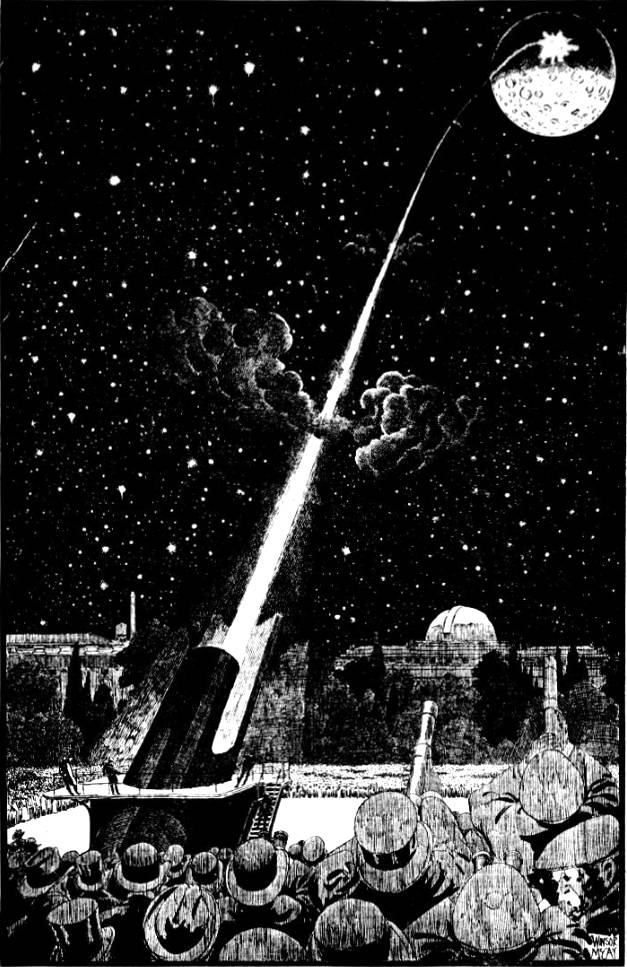

If you pointed your cannon straight up toward the moon, or aimed at the moon your rocket, as Professor Goddard is preparing to do, you would hit the moon if your projectile left the earth at a speed equal to six and seventy-seven-hundreths miles per second. This rate of speed would take the projectile up through the earth’s little air cushion, about two hundred and thirty miles thick, and on beyond to a point in space where the earth’s power of gravitation would end and the moon’s power would begin. The projectile would shoot up the first part of the journey, “fall down” the second part, landing on the moon inevitably. The plan is to charge part of Professor Goddard s rocket with some brilliantly inflammable and explosive stuff, aim it at a dark moon, then watch with telescope and see by the flash that the messenger had struck the moon’s surface and exploded. Continue reading “Shoot the Moon, 1920”